The German eID Function
In the digitalisation of processes in business and public administration, secure electronic identification is of crucial importance in ensuring trust in electronic services.
This trust is what the German eID function was developed to promote. It is based on chip cards (eID cards) that are issued by state authorities and use certified chips and strong cryptographic protocols. These cards include:
- ID cards for German citizens
- Residence permits for people from countries outside of the EU who live in Germany
- eID cards for citizens of the EU and the European Economic Area (EEA)
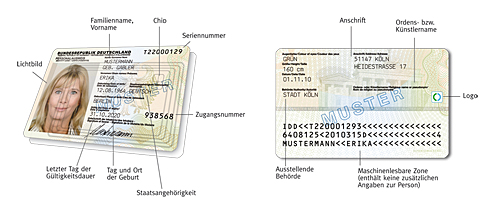

An eID card's chip contains the personal data of the card's holder and plays an integral role in both protecting this data and verifying the holder's identity.
The eID function employs strong two-factor authentication based on possession (that is, of the eID card itself) and knowledge (of the holder's six-digit PIN). Along with the holder's personal data, an eID card contains keys for authentication purposes. The PIN is needed to express the holder's consent and start the authentication process.
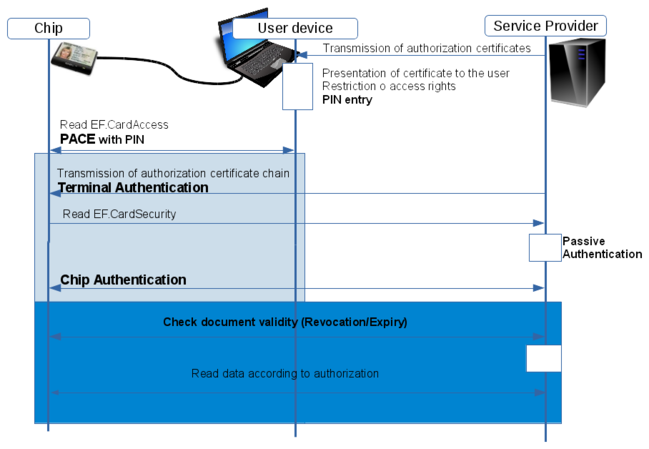
Mutual authentication
In the analogue world, the holder of an ID card usually knows the identity of a person to whom they are identifying themselves. Proof of identity is typically provided directly to the recipient on site and without the involvement of third parties. The eID function transfers this principle into the digital realm. The basic principles of this electronic identification are twofold:
- Mutual authentication -- that is, the chip on a person's eID card authenticates itself to the counterpart in question and the counterpart does the same to the eID card's chip
- Direct communication via a secure channel with end-to-end encryption between the chip of the eID card and the counterpart in question without the involvement of third parties


In this process, data can only be accessed once the counterpart in question has been successfully authenticated and the corresponding access rights have been verified. Unlike in signature-based eID systems, the counterpart does not receive permanent proof of this authentication, which is an advantage in terms of data protection.
Authentication mechanism
The eID function makes use of the General Authentication Procedure (see also: BSI TR 03110).